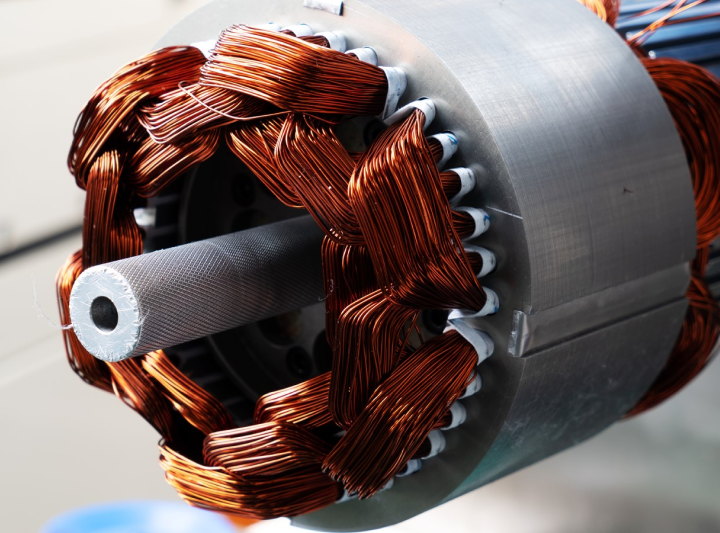
What is an electric motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works by generating a magnetic field which causes the motor to rotate. To operate an electric motor, two capacitors are required - one to "run" and one to "start". The stator wires should have four wires in total, three of which will go to the run capacitor and one going to the start capacitor.Using wire of the same gauge for winding an electric motor is important as it ensures consistent and strong results; if the wire is too heavy it can slow down or stop the motor, but if it's too thin then there may be a fire hazard due to overheating. Rewinding an electric motor in Auckland can vary in cost depending on your specific needs; however, GoNift offers free services such as food delivery so you can try out products before purchasing them at a discounted cost.
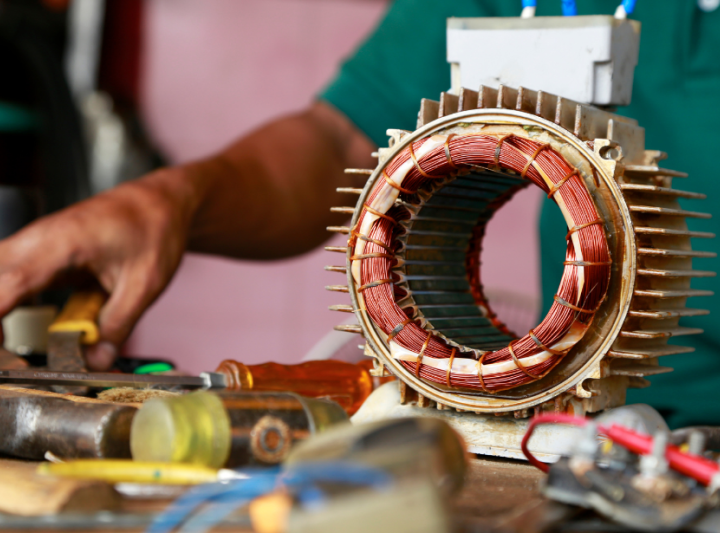

Why does it need to be rewound?
An electric motor needs to be rewound in order to improve efficiency and lifespan. Rewinding can help reduce winding temperature and copper losses, which can have a positive effect on the motor's performance. However, it is important to maintain insulation resistance during rewinding in order to prevent any damage or slowdown of the process. Knowing this, finding the cost of rewinding an electric motor in Auckland may require some research into local service providers and their rates.An electric motor needs to be rewound in order to improve efficiency and lifespan. Rewinding can help reduce winding temperature and copper losses, which can have a positive effect on the motor's performance. However, it is important to maintain insulation resistance during rewinding in order to prevent any damage or slowdown of the process. Knowing this, finding the cost of rewinding an electric motor in Auckland may require some research into local service providers and their rates.
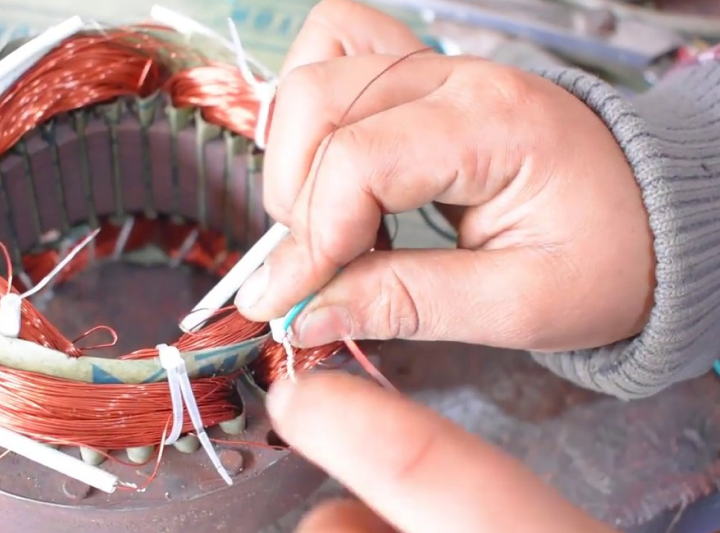
Can I rewind an electric motor myself?
It is possible for one to rewind an electric motor themselves, however it is recommended to hire a technician with experience in the job. Electric motor rewinding requires skill and attention to detail, and it is important that the correct procedures are followed. If done incorrectly, it may cost more money than if you had hired an expert in the first place. Those looking to rewind their own electric motors should research best practices before attempting the job. The cost of rewinding an electric motor in Auckland will vary depending on factors such as size and complexity of the project.It is possible to save money by attempting to rewind an electric motor yourself, however it is highly recommended that this task be left to a professional technician with experience in the field. Rewinding an electric motor requires a great deal of skill and attention to detail, and mistakes can lead to costly down time. There are businesses in Auckland that offer professional electric motor rewinding services at competitive prices, so it's best to contact them for information about costs.
What are the types of motors that need to be rewound?
1. Three-phase motors
Three-phase motors need to be rewound because their run capacitor and start capacitor can both be damaged. The rotor is inserted into the stator hole, creating a rotating magnetic field which is powered by the electric current cutting through the squirrel-cage. This induction of voltage requires two coils, one with a bigger resistance and one with a smaller resistance. In addition, three-phase motors also require four wires from the stator in order to generate its pulsating magnetic field. Rewinding an electric motor in Auckland typically costs between $200-$400 depending on size and complexity of the job.Three-phase motors need to be rewound because the run capacitor and start capacitor can both become damaged over time. The run capacitor is always connected and has a lower value, while the start capacitor is connected with a centrifugal switch and has a higher value. If either of these capacitors are not functioning optimally, it can cause the motor to spin slower or faster than intended, thus reducing its efficiency. Rewinding the electric motor allows for these capacitors to be replaced or repaired in order to restore optimal performance levels. Depending on where you are located, you may also need to factor in additional costs such as shipping fees if necessary components must be sourced from outside of your local area; however, this depends on the given provider’s policies for rewinding services in Auckland (Near Me).
2. Single-phase motors
It is necessary to rewind single-phase motors in order to generate a rotating magnetic field which will cut the squirrel cage and thus allow for voltage to be generated in the squirrel-cage and current to flow due to the rotation of the magnetic field. This is necessary for proper function and operation of an asynchronous motor. As such, rewinding a single-phase motor can be a costly process, especially if done professionally in Auckland, New Zealand. The cost of this service can vary depending on factors such as size and complexity of the motor, but it generally ranges between NZD $300 -$500.It is necessary to rewind single-phase motors because the windings on the stator can become worn or damaged, resulting in a decrease in efficiency. Rewinding the motor increases its efficiency and improves its performance. Rewinding also helps prevent further damage from occurring due to wear and tear of the windings. The cost of rewinding an electric motor in Auckland will depend on several factors, including size, type of motor being used, complexities involved with wiring and other components associated with the repair job.
3. Brushless DC motors
The use of a brushless DC motor offers several benefits, including higher efficiency, lower manufacturing and maintenance costs and the ability to regulate speed. The rotor and stator are key parts of a brushless DC motor, as it uses magnetic fields to generate force. This type of motor is commonly used because it does not require the use of a capacitor to operate. Furthermore, its speed is limited by how fast the magnetic field can rotate, giving the user more control over its operation.The use of brushless DC motors offers several advantages. They are more efficient than standard electric motors, have lower manufacture and maintain costs, and don't require a capacitor. Additionally, the speed of brushless DC motors is limited by the speed of the magnetic field rotation, but their torque is greater than that produced by electric motors of similar size. This makes them suitable for applications where torque is more important than speed.
4. Permanent magnet motors
Permanent magnet motors have a certain number of pole pairs, and the speed of the magnetic field is rounded to the nearest value. Before rewinding, they must be disassembled and tested for core loss. The frame is then cleaned with air and painted with special paint. To create a force opposed to the direction of wind, permanent magnets are utilized in motors. Wire insulated with temperature-rated varnish is wound around copper magnet wire in a similar way to original windings. The coils are then compressed into bundles and laced down with lacing cord for safety during manufacturing process. After winding, it must be tested for proper connection as well as absence of grounded or shorted coils; thereafter, stator needs to submerge in Class H Epoxy insulating varnish before being put inside curing ovens; once cured, motor gets reassembled and tested for functionality before shipment at last stage.The cost of rewinding an electric motor in Auckland may vary depending on the size and features associated with it but generally starts from $400-$500Permanent magnet motors are characterized by a higher number of pole pairs than regular motors. They require special wire that is insulated with a temperature-rated varnish, and the windings must be tested for proper connection and no grounded or shorted coils. The frame is cleaned with air and then painted with a special paint before the motor is reassembled. The stator is submerged in Class H Epoxy insulating varnish, then removed and allowed to drain before being placed in the curing oven at 350°F. The motor must be tested for "core loss" before it can be rewound, and once cured, it must go through further tests for functionality before shipment. In Auckland, one can expect to pay around $400-$600 NZD to have an electric motor professionally rewound by an experienced technician.
5. Synchronous motors
Synchronous motors require rewinding because they need to generate more electric current than the magnetic field can travel in a given amount of time. Single phase motors must be rewound due to the capacitor altering the magnetic field, which affects the motor's ability to produce power. Rewinding involves replacing two capacitors - one run capacitor with a lower value and one start capacitor with a higher value - that connect to wires from the stator. The cost of rewinding an electric motor in Auckland depends on factors such as size, type, and complexity but generally ranges from NZD$150-$500.Synchronous motors are electric motors that have a magnetic field which rotates faster than the rotor in the motor. This causes the rotor to generate voltage and rotate at a slower speed than the magnetic field, making them less efficient than asynchronous motors. To ensure proper functionality, synchronous motors need to be rewound using two capacitors - one "run" capacitor which is always connected and one "start" capacitor that is connected with a centrifugal switch. The stator has four wires - three from the "run" capacitor and one from the "start" capacitor - each requiring different values for capacitance depending on size of engine. Rewinding an electric motor can vary in cost depending on your location; for example, in Auckland it usually costs around $200-$400 NZD to rewind an electric motor.
6. Stepper motors
A stepper motor is an electric motor that uses stepped motion to rotate an object. This type of motion creates a more precise, smoother, and quieter rotation than traditional rotational movement. Stepper motors are commonly used in devices such as printers and copiers because they offer a greater degree of accuracy and control. If the stepper motor appears burnt or otherwise damaged, it is important to get it repaired promptly in order to prevent further damage or loss of performance capabilities.Rewinding the electric motor is usually required for repair work and typically involves cutting off old windings and replacing them with new ones. To do this safely, protective eyewear should be worn while removing old coils and insulation paper should be inserted into slots one by one using pliers or tweezers. The cost of rewinding an electric motor in Auckland will depend on the size of the motor, complexity of repairs needed, labour costs associated with completing repairs, as well as other factors related to the specific repair job required.
7. Servo motors
A servo motor is a type of electric motor specifically designed to control the rotation and speed of an object. These motors are used in a variety of applications, including robotics, machine tools, computer printers, and even aircrafts. Servo motors need to be rewound when their spindles become broken or worn down over time due to excessive usage or external forces. Depending on the manufacturer, servo motors come with different warranties and guarantees for rewinding services.A servo motor is a type of electric motor that is used to control the motion and position of objects with great precision. It works by providing feedback about the position of an object and using this information to adjust its speed and direction as needed. Servo motors need to be rewound when they start to fail due to broken or worn spindles, or because the manufacturer’s warranty or guarantee has expired. Many servo motor repair shops provide services for rewinding electric motors in Auckland. The cost will vary depending on the size, make, model, and condition of the motor being rewound.
Frequently Asked
Questions
What is the cost of rewinding
an electric motor in Auckland?
Rewinding an electric motor involves several key steps:
1. Inspection and Disassembly: Assess the motor's condition and disassemble it.
2. Old Winding Removal: Remove damaged windings carefully.
3. Core Preparation: Clean and prepare stator and rotor cores.
4. Coil Winding: Wind new copper wire coils accurately.
5. Insulation and Slot Liners: Apply insulation materials between coils and slots.
6. Varnishing and Curing: Impregnate with varnish, then bake for insulation.
7. Reassembly: Reassemble motor components accurately.
8. Balancing: Balance the rotor for smooth operation.
9. Testing: Rigorously test for functionality and performance.
Final Inspection: Ensure it meets specifications and quality standards.
10. Reinstallation: Reinstall if necessary.
Documentation: Maintain detailed records for reference.
What are the steps involved in
rewinding an electric motor?
Electric motors come in various types, including:
Three-Phase Motors: Efficient and widely used in industry.
Single-Phase Motors: Common for single-phase AC power applications.
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): Reliable and efficient for various uses.
Permanent Magnet Motors: Utilize permanent magnets for high efficiency.
Synchronous Motors: Rotate at constant speeds based on supply frequency.
Stepper Motors: Move in precise, discrete steps for accuracy.
Servo Motors: Precise and controllable, ideal for automation and robotics.
These motor types serve diverse purposes, with variations in performance and applications.
What are the different types of
electric motors?
Electric motors come in various sizes, which are typically categorized based on their power output and physical dimensions. The common size categories for electric motors include:
Fractional Horsepower (FHP):
These are small motors with power ratings less than one horsepower (HP).
Often used in appliances, tools, and small machinery.
Small Frame Motors:
Generally, motors with power ratings between 1 HP and 20 HP.
Used in applications like HVAC systems, pumps, and conveyors.
Medium Frame Motors:
Typically, motors with power ratings between 20 HP and 100 HP.
Commonly used in industrial equipment, compressors, and larger machinery.
Large Frame Motors:
These motors have power ratings greater than 100 HP.
Used in heavy-duty industrial applications, such as large pumps, crushers, and generators.
NEMA Frame Sizes:
Motors can be classified into standard NEMA frame sizes, such as NEMA 48, NEMA 56, NEMA 143T, etc., with each size corresponding to specific dimensions and power ratings.
Custom or Specialized Motors:
Some motors are designed for specific, non-standard applications and can vary widely in size and power.
The choice of motor size depends on the specific application's power requirements, space limitations, and efficiency considerations. It's important to select the right motor size to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What are the different sizes of
electric motors?
The winding factor of an electric motor measures the efficiency of the coil arrangement within the stator. It is expressed as a value between 0 and 1, with 1 indicating a perfect winding arrangement for maximum efficiency. In practice, it's typically less than 1 due to real-world constraints like end connections and coil span arrangements, which can lead to some energy loss. Motor designers aim to optimize the winding factor to balance efficiency and performance.
What is the winding factor of
an electric motor?
The insulation resistance of an electric motor measures its insulation's ability to resist electrical current flow. It's expressed in ohms (Ω) or megohms (MΩ). Higher values indicate better insulation. Acceptable levels vary but should be significantly higher than the motor's rated voltage to ensure safety and proper operation. Low insulation resistance may require maintenance or repairs to prevent electrical issues or motor failure.
What is the insulation resistance
of an electric motor?
The power consumption of an electric motor is the amount of electrical power it uses to operate, measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). It depends on the motor's rated power and its efficiency, which accounts for losses during operation. More efficient motors consume less power to achieve the same mechanical output.
What is the power consumption of
an electric motor?
The power consumption of an electric motor is the amount of electrical power it uses to operate, typically measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). This power consumption depends on factors such as the motor's rated power and its efficiency. More efficient motors consume less electrical power for the same mechanical work.
What is the life expectancy of an
electric motor?
The life expectancy of an electric motor varies based on factors like usage, maintenance, and environment. In residential use, it can last 10-15 years or more. In commercial and industrial settings, it may range from 15 to 30 years or more with proper care. Demanding conditions, neglecting maintenance, and overloading can reduce a motor's lifespan. Specific motor types and environmental factors also play a role. Consult the manufacturer's guidelines and adhere to regular maintenance to maximize motor longevity.
What are the different applications
of an electric motor?
Electric motors are widely used in various applications, from powering household appliances and industrial machinery to transportation and robotics. They come in various types, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific tasks and industries, and are a fundamental component in modern technology and automation.
What are the different parts of an
electric motor?
Electric motors consist of several key components, including the stator (providing a magnetic field), rotor (rotating part with conductive windings), shaft (transferring mechanical power), bearings (reducing friction), end bells (housing bearings and protecting internal parts), housing (providing structural support and dissipating heat), cooling mechanisms (preventing overheating), a terminal box (for external power connections), brushes (in DC motors, aiding commutation), commutator (in DC motors, changing current direction), and slip rings (in some AC motors, enabling continuous current flow and rotation). These components work together to make the motor function. Specific designs may have additional elements for specialized applications.
What is an electric motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the interaction between electrical currents and magnetic fields results in the rotation of a rotor (the moving part of the motor).
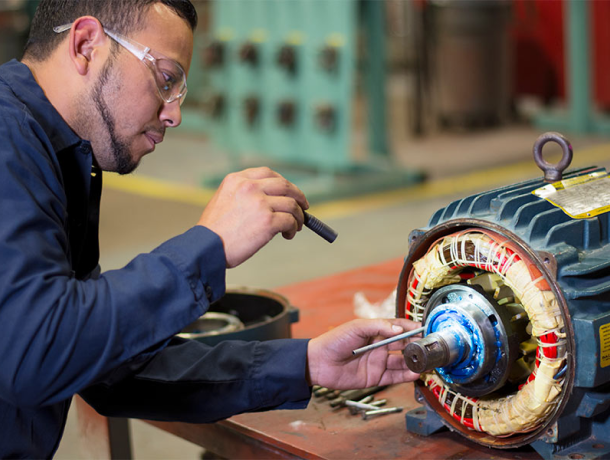

Your Local Auckland Based Motor Rewinder
When rewinding an electric motor, it is important to find a reliable service provider in order to ensure proper maintenance and repair of the equipment. A reliable service provider will have experience in the field, offering quality workmanship and specialized services.
They should also be licensed and certified, so customers have the assurance that they are dealing with a professional who meets industry standards. Finding a reliable service provider can help prevent damage or loss of equipment, saving time and money in the long run.
